Better overview on the typical computer hardware.
Typical PC hardware
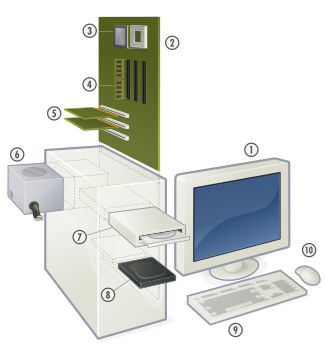
1. Monitor
2. Motherboard
3. CPU
4. RAM Memory
5. Expansion card
6. Power Supply
7. CD-ROM Drive
8. Hard Disk
9. Keyboard
10. Mouse
Though a PC comes in many different form factors, a typical personal computer consists of a case or chassis in a tower shape (desktop) and the following parts: You can find out more at http://www.hardware.com/
Motherboard
The motherboard is the "brain"[citation needed] of the computer. Components directly attached to the motherboard include:
- The central processing unit (CPU) performs most of the calculations which enable a computer to function, and is sometimes referred to as the "brain" of the computer. It is usually cooled by a heat sink and fan.
- The chipset mediates communication between the CPU and the other components of the system, including main memory.
- RAM Stores all running processes (applications) and the current running OS. RAM Stands for Random Access Memory
- The BIOS includes boot firmware and power management. The Basic Input Output System tasks are handled by operating system drivers.
- Internal Buses connect the CPU to various internal components and to expansion cards for graphics and sound.
- Current
- The northbridge memory controller, for RAM and PCI Express
- PCI Express, for graphics cards
- PCI, for other expansion cards
- SATA, for disk drives
- The northbridge memory controller, for RAM and PCI Express
- Obsolete
- Current
- External Bus Controllers support ports for external peripherals. These ports may be controlled directly by the southbridge I/O controller or based on expansion cards attached to the motherboard through the PCI bus.
Power supply
Includes power cord, switch, and cooling fan. Supplies power at appropriate voltages to the motherboard and internal disk drives. It also converts alternating current to direct current and provides different voltages to different parts of the computer.
Video display controller
Produces the output for the visual display unit. This will either be built into the motherboard or attached in its own separate slot (PCI, PCI-E, PCI-E 2.0, or AGP), in the form of a graphics card.
Removable media devices
- CD (compact disc) - the most common type of removable media, suitable for music and data.
- CD-ROM Drive - a device used for reading data from a CD.
- CD Writer - a device used for both reading and writing data to and from a CD.
- DVD (digital versatile disc) - a popular type of removable media that is the same dimensions as a CD but stores up to 12 times as much information. It is the most common way of transferring digital video, and is popular for data storage.
- DVD-ROM Drive - a device used for reading data from a DVD.
- DVD Writer - a device used for both reading and writing data to and from a DVD.
- DVD-RAM Drive - a device used for rapid writing and reading of data from a special type of DVD.
- Blu-ray Disc - a high-density optical disc format for data and high-definition video. Can store 70 times as much information as a CD.
- BD-ROM Drive - a device used for reading data from a Blu-ray disc.
- BD Writer - a device used for both reading and writing data to and from a Blu-ray disc.
- HD DVD - a discontinued competitor to the Blu-ray format.
- Floppy disk - an outdated storage device consisting of a thin disk of a flexible magnetic storage medium. Used today mainly for loading RAID drivers.
- Zip drive - an outdated medium-capacity removable disk storage system, first introduced by Iomega in 1994.
- USB flash drive - a flash memory data storage device integrated with a USB interface, typically small, lightweight, removable, and rewritable. Capacities vary, from hundreds of megabytes (in the same ballpark as CDs) to tens of gigabytes (surpassing, at great expense, Blu-ray discs).
- Tape drive - a device that reads and writes data on a magnetic tape, used for long term storage and backups.
Internal storage
Hardware that keeps data inside the computer for later use and remains persistent even when the computer has no power.
- Hard disk - for medium-term storage of data.
- Solid-state drive - a device similar to hard disk, but containing no moving parts and stores data in a digital format.
- RAID array controller - a device to manage several internal or external hard disks and optionally some peripherals in order to achieve performance or reliability improvement in what is called a RAID array.
Sound card
Enables the computer to output sound to audio devices, as well as accept input from a microphone. Most modern computers have sound cards built-in to the motherboard, though it is common for a user to install a separate sound card as an upgrade. Most sound cards, either built-in or added, have surround sound capabilities.
Other peripherals
In addition, hardware devices can include external components of a computer system. The following are either standard or very common.
Includes various input and output devices, usually external to the computer system.
Input
- Text input devices
- Pointing devices
- Mouse - a pointing device that detects two dimensional motion relative to its supporting surface.
- Optical Mouse - a newer technology that uses lasers, or more commonly LEDs to track the surface under the mouse to determine motion of the mouse, to be translated into mouse movements on the screen.
- Trackball - a pointing device consisting of an exposed protruding ball housed in a socket that detects rotation about two axes.
- Gaming devices
- Joystick - a general control device that consists of a handheld stick that pivots around one end, to detect angles in two or three dimensions.
- Gamepad - a general handheld game controller that relies on the digits (especially thumbs) to provide input.
- Game controller - a specific type of controller specialized for certain gaming purposes.
- Image, Video input devices
- Image scanner - a device that provides input by analyzing images, printed text, handwriting, or an object.
- Webcam - a low resolution video camera used to provide visual input that can be easily transferred over the internet.
- Audio input devices
- Microphone - an acoustic sensor that provides input by converting sound into electrical signals.
- Mic - converting an audio signal into electrical signal.



0 comments:
Post a Comment